Description
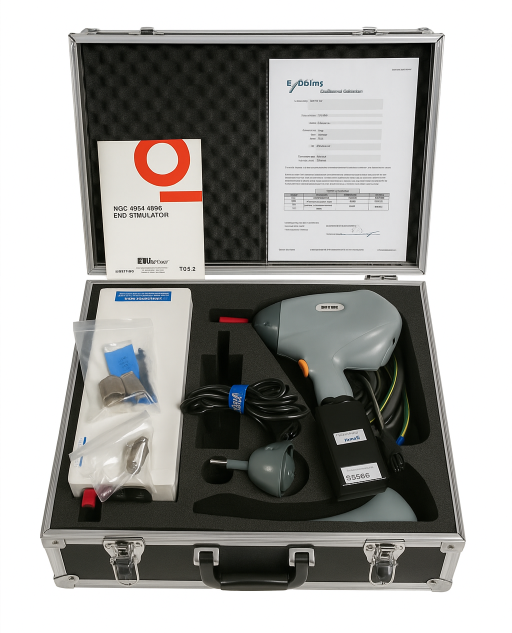
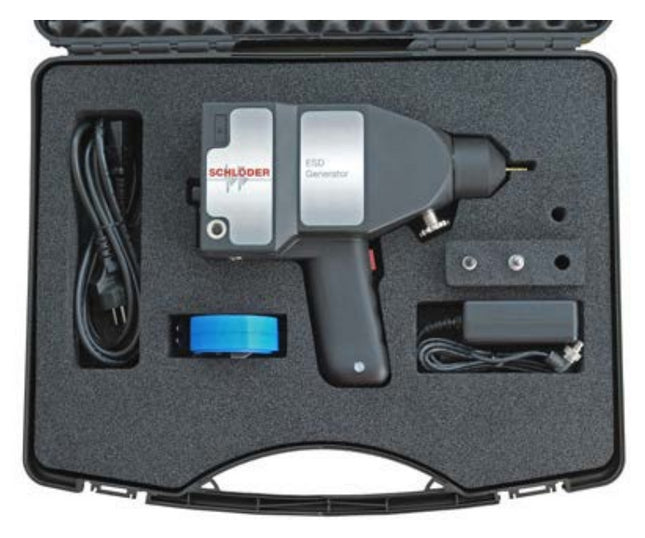
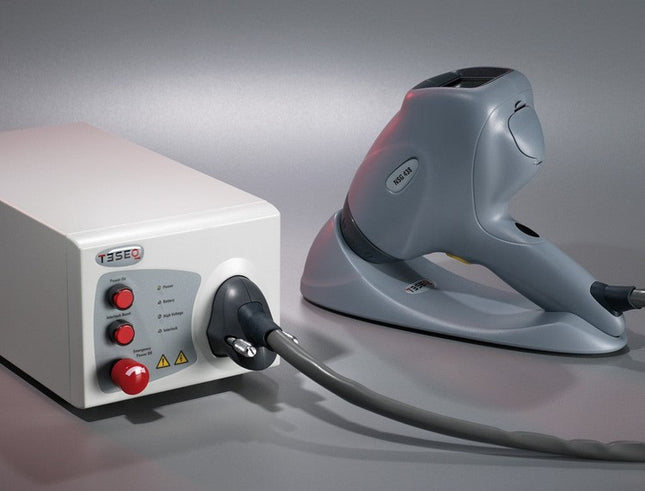
ESD16 16.5kV ESD Simulator for IEC/EN 61000-4-2
The ESD16 16.5kV ESD Simulator is suitable for performing EMI tests on systems in accordance with the standard IEC / EN 61000-4-2 , MIL-STD-461G CS118, RTCA/DO-160 Section 25, IEC 60601-1-2 and many other ESD test standards. Higher test levels can be set far beyond the standard limits. Depending on the test object and test setup, two test methods are to be used:
-
Air Discharge
In this case, the pulse is triggered by approaching the ESD16 towards the DUT. The high voltage applied to the discharge electrode is discharged suddenly, resulting in a very broadband highfrequency interference spectrum. This in turn can lead to influences on the test specimens.
-
Contact Discharge
With this method, the probe of the generator is placed directly on the test object. The actual "impulse triggering" takes place via a relay contact and reduces the influencing factors such as approach speed, amplitude height, air humidity and temperature.
Important: In the case of non-contacting (eg painted or oxidized surface), the impulses are not triggered. The display shows "No contact". This ensures that when triggering a discharge actually takes place.
The contact discharge is the preferred test method since it is most reproducible. Air discharges are used when contact discharges are not possible - e.g. at plastic housings. The test voltages defined for each test method are shown in the table below: